As I stated in an earlier blog, skin color is determined by the pigment melanin. Everybody has the same number of melanocytes in their body. The difference is the type of melanin that people have. Eumelanin is the darker pigment and pheomelanin is the orange pink or lighter melanin.
The melanocyte is a cell that contains melanosomes in the cytoplasm. The melanosomes produce the melanin pigment. The melanosome is transferred to the upper layers of the epidermis by the keratinocytes. One melanocyte is supported by 36-40 keratinocytes. When this ratio in off, hyperpigmentation can exist.
Lighter skin people have more pheomelanin than eumelanin. The pheomelanin does not protect the skin against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) as well as the eumelanin. A Fitzpatrick 6 patient which is the darkest skin one sees will get a SPF 15 effect on their skin for 2 hours just by their pigment. After that time, the patient will burn and can get sun damage and could potentially get melanomas or other skin carcinomas just like lighter skinned people.
This brings me to the point of talking about SPF. Most SPF blocks will protect agains UVB rays which causes one to burn and produce a tan for a short amount of time. For a sunblock to be effective, one needs a broad spectrum block that also protects against UVA, UVB and UVC rays. UVA rays cause a tan of longer duration with no burning of the skin.
Most of the exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) occurs durning the hours of 10 am to 4 pm. For sun blocks to be effective, one needs to reapply them 3-4 times / day. Most patients only apply them once in the morning. This is one of the reasons pigment will recur on their face.
Another misconception is the amount of protection we gets from different SPF blocks.
- SPF of 15- gives 96% protection
- SPF of 30- gives 97% protection.
- SPF of 50- gives 98% protection.
- SPF of 100- gives 98.2% protection.
As you can see a good broad based sunblock of SPF 15 that is water resistent and water proof give pretty good protection. As the SPF is doubled, the protection only goes up by 1% at most.
In my last blog on hyper-pigmentation, I showed the pathways of melanin synthesis which is quite complex and controlled by 250 genes.
Hyper-pigmentation includes the following conditions.
- Tanning.
- Facultative which is uneven skin tone that starts around age 30.
- Ephelides are freckles which are caused by a genetic mutation that effects mostly in
- Fitzpatrick 2 skins. These patients get speckled hyper-pigmentation in areas of sun exposure and usually have an even distribution.
Post-inflammatory hyper-pigmentation can occur after some type of injury to the skin. This has a genetic predisposition and is common in Indo-Pakistani, South East Asian Middle Eastern, and Mediterranean descent patients.
Melasma is also very common in the above type of patients and can be triggered with increased estrogen and sun exposure. Typically, 98% of patients that have melasma are female and 2% are male which usually have Addison’s Disease or are of Chinese descent. The most common areas where the pigmentation occurs is the forehead, cheeks, and upper lips.
Treatment of melasma can be difficult and one really just controls the pigmentation and does not cure it.
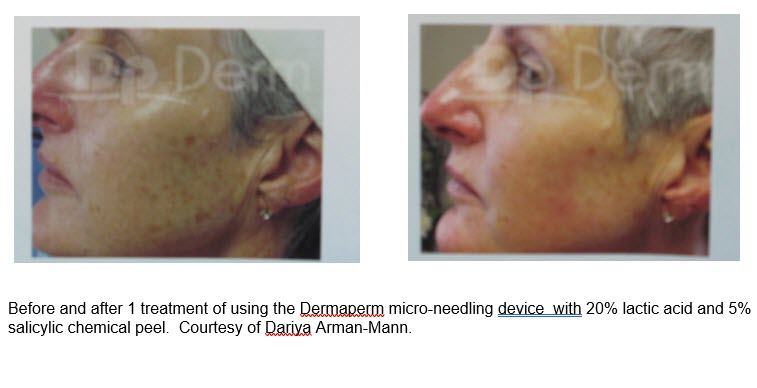
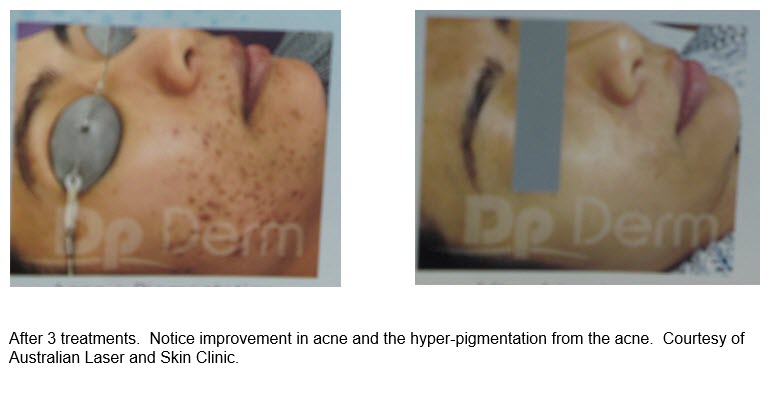
Micro-needling has been shown to successfully treat hyper-pigmentation.
It has been shown to :
- Activate the following growth factors: MGF, KGF and EGF ( melanocyte, keratinocyte and epidermal growth factors). These improve melanogenesis and epidermal function.
- There is normalization of signaling between the keratinocytes and melanocytes. The transfer between the melanocytes and keratinocytes is regulated and the ratio of one melanocyte to 36-40 keratinocytes is maintained.
- Mitogen -activated protein kinase also normalizes the function of the melanocyte and dendrite arms.
- Infusion of substances into the upper dermis where abnormal melanocytes are located with bleaching creams will accelerate the bleaching effect.
- There will be increased absorption of chemical peels which can be used as a combination treatment with micro-needling.
In summary, abnormal pigmentation is a complex subject and usually difficult to treat.
There is usually an abnormality in the production of melanin and transfer of it. There are certain triggers that sometimes can be minimized like sun exposure with the use of a proper sunblock and repeated applications. Micro-needling will stimulate certain growth factors that can improve the function of the cells in the skin and it will also create channels that allow for penetration of agents to areas where the abnormal cells are located. Continued use of bleaching agents along with combination treatments like chemical peels will give better results in a shorter amount of time.